The implementation of the TRIPS agreement resulted in significant changes in how governments enforced intellectual property rights. As a result, business owners and entrepreneurs began to place a premium on their brand names and trademarks. The increase in the number of applications for trademark registration coincided with an increase in the number of infringement cases, in which tiny enterprises attempted to replicate and profit off the goodwill and repute of previously existing trademarks.
This eventually led to higher courts taking infringement cases and setting precedent for future cases to follow. This article also provides a summary of famous trademark infringement cases in India that have served as a model for similar lawsuits.
Table of Contents
ToggleFamous Trademark Infringement Cases in India
Here are some examples of trademark infringement cases from India that illustrate the nuances of the relevant legislation.
1. Yahoo! Inc. v. Akash Arora & Anr: One of the earliest cases of Cybersquatting in India

This case is one of the most famous trademark infringement cases in India. In addition to trademark infringement, it is often asked that the case of Yahoo! Inc. V. Akash Arora belongs to which dispute outside trademark infringement? The correct response is ‘Cybersquatting’; this is one of the earliest known instances of cybersquatting.
Factual Background
Yahoo INC., the plaintiff, was the owner of the trademark “Yahoo” and the domain name “yahoo.com,” both of which were widely recognized brands in the minds of consumers around the world providing internet services. In addition Yahoo was a registered company since 1995, having registered trademarks in various countries except India.
Akash Arora, the defendant in the particular case simultaneously started using the domain name ‘yahooindia.com’ for the similar kind of services India. Yahoo Inc. sought an interim injunction to prevent from using the domain name ‘yahooindia.com’ or any name similar to its own.
Decision of the Court
The court determined that Akash Arora was liable for infringing the “Yahoo” trademark and restricted him on the basis that he was using a deceptively similar domain name and delivering services similar to those of Yahoo Inc., which constituted cybersquatting. This ruling was based on the premise that a company’s goodwill resides primarily in its name and trademark, and especially so in the instance of Yahoo Inc. Yahoo Inc. was awarded the passing-off remedy.
2. Amazon v. Happy Belly Bakes: Trademark Rights of small business owners against the Giant ones

Factual Background
Shisham Hinduja founded Happy Belly Bakes in 2008, a women-owned business that sells baked items like cakes, brownies, cookies etc. It has owned the trademark for the name ‘Happy Belly’ since 2016, (before it was known as Regalar and it switched to Happy Belly Bakes in 2010).
Happy Belly Bakes used the trademark since its inception in 2008. It sued Amazon for selling bakery items, snacks, and dairy under the same brand name.
In 2016, the bakery began receiving calls asking if their products were available on Amazon. However, the website of the e-commerce giant revealed that Happy Belly was Amazon’s own brand for selling bakery products. Tootsie LLC filed the trademark application on behalf of the e-commerce firm, arguing that while Happy Belly Bakes only operated in Bengaluru, Amazon sold the products worldwide.
Decision of the Court
The court held that Amazon had infringed the trademark of Happy Belly Bakes. The court gave verdict in favour of Happy Belly Bakes against Amazon. It took four years for Happy Belly to get justice but at the end they were able to protect their trademark against the tech giant – Amazon. While the small businesses struggle to get justice against giant enterprises, this case of Happy Belly Bakes showed that the infringement laws are for all and are common.
3. The Coca-Cola company v. Bisleri International Pvt. Ltd: Assignment of Trademarks

Factual Background
Coca-Cola v. Bisleri case study is amongst the major trademark infringement cases in India. The plaintiff is the largest soft drink brand in the world, with a presence in 200 countries, whereas the defendant is a very well-known Indian brand recognized for its bottled water. In September 1993, the defendant sold the plaintiff the rights to the soft drink MAAZA. In March 2008, the plaintiff submitted a trademark application for the name “MAAZA” in Turkey. In September 2008, the defendant sent the plaintiff a legal notice revoking the licensing agreement and announcing its desire to begin using the trademark in India. Both directly and indirectly, the defendant was involved in the manufacture, sale, and exportation of MAAZA-branded items.
Decision of the Court
A temporary injunction was issued against the defendant. The Honorable Court decided that the plaintiff had both a prima facie case and a favorable balance of conveniences. The rejection of the trademark was deemed invalid, and the plaintiff was given complete trademark rights for the soft drink MAAZA. It was determined that the defendants were responsible for trademark infringement.
4. Daimler Benz Aktiengesellschaft & Anr. v. Hybo Hindustan: Dilution of Well-known trade marks

Factual Background
In this case, an undergarments shop used the term ‘Benz’ in the title of the brand, as well as a logo that looked suspiciously similar to the logo created and used by the car company. The famous three-star ring of Mercedes Benz which is very popular across the globe was used by the defendant for selling undergarments. The defendant was using a three-pointed human being in a ring as his logo. The plaintiff got to know this and filed the case against the defendant.
Decision of the Court
It was held by the court that this is a clear infringement of the trademark as the three-star ring of the Mercedes is a well-known mark and is widely known across the world for the cars. Therefore, the defendant was refrained from using this mark by an injunction. The court in this case had acknowledged the trademark’s international reputation, remarking that almost no one would ever fail to associate the word “Benz” with the car. As a result, no one can claim that he was unaware of the use of the mark “Benz” which is popularly known to have in relation to automobiles.
5. Starbucks Corporation v. Sardarbuksh Coffee & Co.: Rule of Dominant Feature of a Trademark

In this specific case, the meaning and fundamental nature of a trademark were reaffirmed; namely, that a trademark is a one-of-a-kind identifier and distinguishing feature for both the customer and the company in question.
Factual Background
Starbucks registered their word mark ‘STARBUCKS’ and corresponding logo as a trademark in India in 2001. The Defendants established their business in 2015 under the name ‘Sardarbuksh Coffee & Co.’ Sardarbuksh’s logo was a turban commander’s face with wavy lines on the sides surrounded by a circular black band. Through a letter of demand, the Plaintiff requested that the Defendants change the logo in 2017. In response, the Defendant simply changed the colour scheme to black and yellow and resumed operations. The Defendant began operations under the same name in May 2018. The Defendant and Plaintiff provide comparable goods and services. The plaintiff filed a suit against Sardarbuksh in the Hon’ble High Court of Delhi as a result of the preceding events. The plaintiffs sued the defendants for trademark infringement by using a deceptively similar mark.
Decision of the Court
The Delhi High Court relied on the National Sewing Thread Co. decision. Ltd vs James Chadwick & Bros Ltd, which stated that in order to determine whether a trademark was deceptively similar, the court had to put itself in the shoes of the customers.
The Delhi High Court concluded, using the aforementioned case that a man of ordinary intelligence might be confused, and thus it is deceptively similar.
6. Mondelez India Foods Private Limited (formerly Cadbury India Ltd.) V. Neeraj Food products: Attempt to free ride on the goodwill of well-known trademarks using deceptively similar marks

Factual Background
The plaintiff, Cadbury India Limited, filed a lawsuit seeking permanent and mandatory injunction against the defendant’s deceptively identical mark and goods/products. The plaintiff alleged that the defendant sold chocolate with the trademark ‘JAMES BOND’ that was deceptively similar to their trademark ‘Cadbury GEMS’ with similar packaging and was inspired by Cadbury’s famous fictional character & registered copyright ‘GEMS BOND’ from the plaintiff’s advertising campaign in the late 1980s and early 1990s. The plaintiff also alleged that the defendant is trying to create confusion in the mind of consumer so as to free ride on the goodwill of the former.
Decision of the Court
The Delhi High Court upheld the decision in the favour of the plaintiff. In addition to the relief of a permanent and mandatory injunction granted to the Plaintiff, the court awarded the Plaintiff damages in the amount of Rs. 10 lakhs.
7. Cadila Healthcare Ltd. V. Cadila Pharmaceuticals: Trademark should be read in its entirety
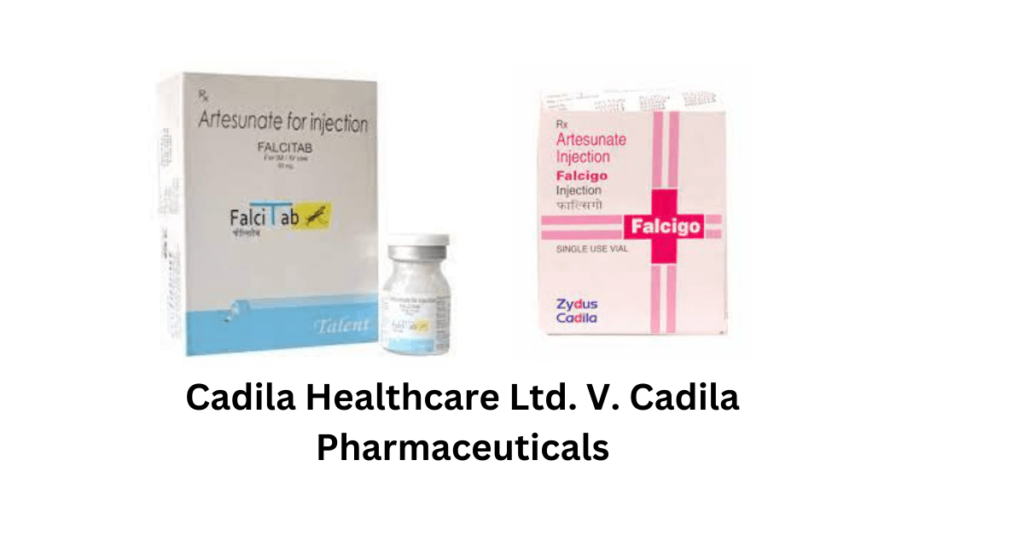
Factual Background
The appellant (Cadila Healthcare) and the defendant (Cadila Pharmaceuticals) were two pharmaceutical companies that introduced medicine for the treatment of cerebral malaria. The appellant launched the medicine in style and name of ‘Falcitab’ and the respondent launched it in the name ‘Falcigo’. Cadila Healthcare filed the lawsuit after discovering that Cadila Pharmaceutical is using the mark “FALCITAB” which is similar to their mark “FALCIGO”; and that Cadila Pharmaceutical registered the mark for a similar medicine. In this lawsuit, Cadila Healthcare sought an injunction prohibiting Cadila Pharmaceutical from using a mark that is deceptively similar and likely to cause confusion amongst the consumers.
Decision of the Court
The Hon. Supreme Court held that even though the drug is to be prescribed by the medical practitioners and sold directly to hospitals, the possibility of the confusion between the two cannot be disregarded.
The Supreme Court also held that there are certain principles that need to be followed in the case of deciding the mark as a deceptively similar. They are as follows:
- To check the nature of the marks which includes word marks composite marks etc.
- To check ideological and phonetic similarity
- To check the similarity of nature, performance, and character of applicants
- To identify the class of consumers etc.
8. Toyota Jidosha Kabushiki Kaisha v. M/S Prius Auto Industries Ltd. – Trans-border reputation of Trademarks
Factual Background
The plaintiff, Toyota alleged that the defendants, Prius Car Industries, a supplier of auto parts and accessories, infringed upon its registered ‘Toyota,’ ‘Toyota Innova,’ ‘Toyota Device,’ and ‘Prius’ Trade Marks. The plaintiff petitioned the Trade Mark Registry for cancellation of the defendants’ registered mark, and filed suit on the grounds that the defendant was using their “well-known mark” without their permission, resulting in an unfair benefit to the plaintiff’s reputation and goodwill. On the other hand, The Plaintiff did not register the “Prius” trademark in India, and its Prius automobile was not introduced in India until 2009, much after the Defendant registered the “PRIUS” trademark in India in 2002.
Decision of the Court
The Supreme Court determined that “likelihood of confusion” and the differentiating powers of a man of average intelligence would be a more appropriate standard for proving a passing-off activity, which can only be proven by evidence, which the Appellants failed to offer. Toyota Jidosha Kabushiki-trademark petition was dismissed after the Supreme Court ruled that trademark rights are territorial and not universal and that actual proof is required to establish a company’s reputation and goodwill in a territory.
9. Nandhini Deluxe v. Karnataka Co-Operative Milk Producers Federation Ltd. – no one can claim an exclusive right or monopoly over an entire class of goods

Factual Background
The respondents, Karnataka Co-operative Milk Producers, had been using the mark for milk and related products registered under class 29 since 1985. Appellant Nandhini Deluxe is a restaurant chain in Karnataka that used the mark in 1989. The Appellant has applied for registration of the said mark in class 29 for meat, fish, poultry, meat extracts, preserves, dried and cooked fruits and vegetables, jellies, jams, eggs, milk and milk products, edible oils and fats, salad dressings, and so on. The registrar approved the registration of the mark ‘Nandhini’ as distinct from the existing mark. The IPAB and the High Court of Karnataka both found the marks ‘Nandini’ and ‘Nandhini’ to be deceptively similar, with the only difference being the letter ‘H’ between the two marks.
Decision of Court
The case was ultimately heard by the Supreme Court, which determined that the marks are not deceptively similar after a thorough examination of both. The court noted that there is only a phonetic similarity between the two marks Nandini/Nandhini. Aside from that, the logos for both marks are distinct. The phrase ‘Deluxe’ was used by the restaurant and is followed by the words ‘the real spice of life,’ whereas the mark Nandini has no suffixes or prefixes. The Supreme Court concluded that no one can claim an exclusive right or monopoly over an entire class of goods, especially when the trademark is not used with respect to all of the goods in that class. Finally, the appellant ‘Nandhini Deluxe’ was granted permission to use the mark after removing milk and milk products from their class description.
10. Amritdhara Pharmacy V. Satya Deo Gupta: Monopoly over the generic terms can’t be allowed & the concept of honest concurrent use.

Factual Background
The respondent, Satya Deo Gupta, submitted an application to register the name “Lakshmandhara”, which has been in the business of selling and preparing medicinal items since 1923. “Amritdhara” the appellant company Amritdhara Pharmacy, objected the registration of the term Lakshamandhara on the grounds that it is likely to mislead and confuse clients due to the appellant’s trademark Amritdhara, which has been in the same line of business since 1901. In response, the defendant filed a counter-affidavit claiming concurrent usage on the basis that they had been using the mark since 1923.
Decision of the Courts
The Registrar of Trademarks determined that Amritdhara and Lakshmandhara are sufficiently similar to cause confusion. The Allahabad High Court on appeal, granted the respondent’s appeal, allowing registration of the mark “Lakshmandhara” while denying the appellant’s appeal and stating that the marks are dissimilar. The court also ruled that the words “Amrit” and “Dhara” cannot be monopolized because they are part of the common language. The High Court discovered insufficient grounds to deny the Lakshmandhara trademark registration. The case was then brought before the Supreme Court on appeal.
The Supreme Court reversed the High Court’s decision that Amritdhara and Lakshmandhara are comparable marks. The court relied on the comparison of marks test and stated that the question of comparing two marks should be viewed from the perspective of a man with average intelligence and defective recall.






