Intellectual property brings whole lot of benefits. It turns an idea into an profit-making asset, enhances the market value of a business and even helps for raising finances. Patent is one such form of intellectual property. Before we analyze the patent filing procedure in india, let us analyze what is patent? And what is the importance of it.
A patent is an exclusive right granted for an invention (either a product or a process) that provides, a new way of doing something, or offers a new technical solution to a problem. The patent gives its owner the legal right to exclude others from using, making, or selling an invention for a limited period in exchange for publishing an enabling disclosure of the invention.
A patent, granted by the government i.e. patent office, provides an exclusive right to an inventor to make, use, and sell his invention. This exclusive right is valid for a time period of 20 years from the date of filing.
Interesting facts
Following are the two ways an inventor or person can file a patent:
- The inventor can file the patent on his/her own
- The inventor can take the help of a patent filing expert or an organization.
Since the patent filing process is long and complicated, most inventors prefer to engage the services of expert patent filing professionals or service providing organizations. Such individuals or firms charge a fee since they have years of experience/ expertise. They can complete the necessary patent filing procedures on the behalf of an inventors.
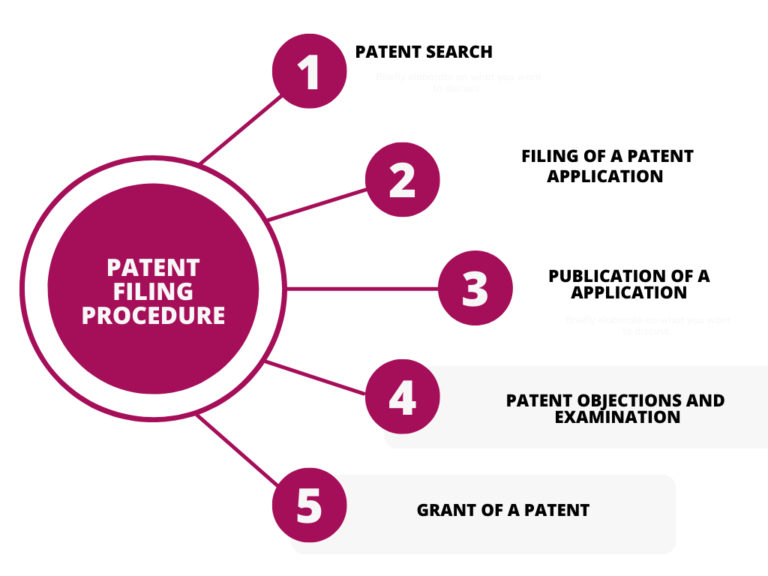
Following are the steps for filing patent in India
Step 1 – Conceiving the idea or invention
The first step for an inventor/person who wants to go ahead with his or her invention is to compile or collect as much related information as possible. Some of the pertinent questions that the inventor/person must think are: the field of the invention, advantages, how will it help in improving already existing solutions/products/processes (and the like)?
Step 2 – Check if the idea or invention is new
Before an inventor/person begins the patent registration process, it is advisable to check if the invention is patentable. This means that it must be checked if another individual or organization has filed a patent for a similar technology for which an inventor/person is filing. Performing an in-depth patentability search helps you understand whether or not the inventor/person have a chance of getting a patent. While this step is optional, it can save time and help the inventor/person to understand whether or not patent should be filed.
Interesting facts
Before filing a patent application, one must check the patentability of their invention. Slight variations in the patentability eligibility criteria can be seen based on the jurisdiction. Main criteria for patentability are as follows:
Novelty: The invention should be new with no public disclosures in any part of the globe or through any other platform.
Non-obvious: No skilled person in the relevant area of technology should be able to decode the invention easily. The invention must be having distinctive value-adding feature compared to existing inventions in the same field
Business or industrial application: The newly invented product or process should have a wide range of industrial utilities with positive economic implication
Step 3 – Drafting Patent Application
The next step which follows requires effective drafting of the patent application. The application consists of various parts such as claims, background, description, drawing (if any), claims, abstract, and summary. The aforementioned portions of specification/patent application must be carefully drafted to provide effective disclosure of the invention. While drafting the patent application utmost care and precision must be taken.
In case the invention is still in idea stage an inventor/person can draft and file a provisional patent application to protect idea ad to get priority over other competitors. In case of provisional patent application claims will not be there in patent application.
Also an inventor, can either draft patent application by himself or can seek professional drafters help.
Step 4 – Filing the Patent Application before Indian patent Office (IPO)
After drafting the patent application, it is filed in the government patent offices as per the application form in Form 1/jurisdiction. A receipt is be generated with the patent application number. A person/inventor can also file a provisional patent application, if the invention is at an early stage (idea stage without any form of prototype or definitive process).
The advantage of filing a provisional application is that the person/inventor can secure a prior date of filing which is crucial in the patent world. Also, the person/inventor gets 12 months’ time to file the complete specification (patent application).
Step 5 – Patent Application Publication
After filing the complete specification, the application is published after 18 months from the date of filing. There is no need for any special requirement from the applicant for publication. However, if the applicant does not want to wait till the expiry of 18 months, an early publication request can be filed along with prescribed fees by filing Form 9. The patent application is published within one month from the request of early publication.
Step 6 – Request for examination (RFE)
The examination is not an automatic process like publication and the applicant is required to request the patent office to examine the patent application. A normal request for examination (RFE) must be filed by 48 months from the date of filing of the patent application, under Form 18. After the RFE is filed, the controller provides the application to a patent examiner.
The patent examiner examines it with different patentability criteria i.e. novelty, non-obviousness or inventive step, and capable of industrial applicability. After examining the patent application the examiner provides the applicant with a First Examination Report (FER). The application can also file a request for expedited examination of the application under Form 18A.
Step 7 – Responding to objections/examination report
The applicant is required to submit a written response to the raised objections in the examination report. The applicant can argue regarding the patentability of the invention and try negating the objections being raised by the examiner. Physical hearing or video conferencing can also be requested, as per requirement and norms.
Step 8 – Patent Grant
After addressing all objections, the patent application would be placed for a grant once it is found to be meeting all patentability requirements, and finally, the patent will be granted to the applicant. The grant of a patent is notified in the patent journal which is published from time to time.
Any interested person or organization can file a post-grant opposition within 12 months from the date of publication of the granted patent (by submitting a notice of opposition to the controller).
Step 9 – Patent life term and renewal of patent
Usually, a patent holds a validity for 20 years. After 20 years, the patent owner is required to renew the patent by paying corresponding fee.
Conclusion
Although the patent filing process and registration seems to be long and tedious, a person must remember its importance in the long run. The entire process may take couple of years. However, Indian Patent Office is upgrading its offices and process to be able clear of patent applications in timely manner.
The process is created with the intention of ensuring that the inventor gets credit for his invention such that no other individual can claim rights over the invention. The legal rights earned by an individual/organization regarding patent can prevent competitors from using your invention for financial benefits. The patent holder can also sue such individuals and claim compensation for using invention without approval.